Page 72 - 2025 Special Report
P. 72
2. An overview of elderly care policies economic backgrounds of these societies. In
in the Greater Bay Area cities Hong Kong and Macau, elderly care provisions
emphasize social security measures, including
There is a global trend of an aging population, economic assistance and provident funds.
making elderly care a central focus in policymaking for These systems aim to provide economic
many communities. The population and dependency security for the senior population, while also
ratios of the senior population aging 65 years and protecting their economic and social welfare.
above in the GBA cities have shown an upward trend In contrast, Guangdong Province’s elderly care
between 2010 and 2020. This increase has been most system is based on the concept of “rooted
notable in Hong Kong and Macau, leading to a higher in home-living, with social assistance and
demand for local health care and elderly care services. institutions as the support,” replying on family
and community as the primary care units. The
The unique characteristics of elderly care focus here is on strengthening of family-based
services in each GBA city reflect the different elderly care.
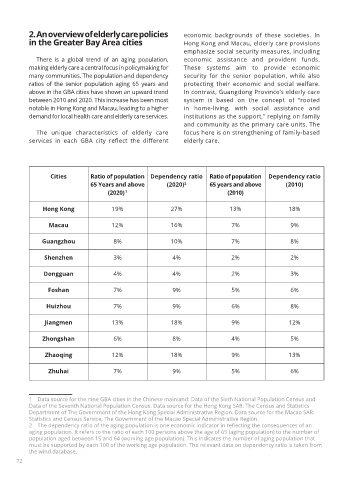
Cities Ratio of population Dependency ratio Ratio of population Dependency ratio
65 Years and above (2020) 65 years and above (2010)
2
(2020) (2010)
1
Hong Kong 19% 27% 13% 18%
Macau 12% 16% 7% 9%
Guangzhou 8% 10% 7% 8%
Shenzhen 3% 4% 2% 2%
Dongguan 4% 4% 2% 3%
Foshan 7% 9% 5% 6%
Huizhou 7% 9% 6% 8%
Jiangmen 13% 18% 9% 12%
Zhongshan 6% 8% 4% 5%
Zhaoqing 12% 18% 9% 13%
Zhuhai 7% 9% 5% 6%
1 Data source for the nine GBA cities in the Chinese mainland: Data of the Sixth National Population Census and
Data of the Seventh National Population Census. Data source for the Hong Kong SAR: The Census and Statistics
Department of The Government of the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region. Data source for the Macao SAR:
Statistics and Census Service, The Government of the Macao Special Administrative Region.
2 The dependency ratio of the aging population is one economic indicator in reflecting the consequences of an
aging population. It refers to the ratio of each 100 persons above the age of 65 (aging population) to the number of
population aged between 15 and 64 (working age population). This indicates the number of aging population that
must be supported by each 100 of the working age population. The relevant data on dependency ratio is taken from
the wind database.
72 73